|
|
|
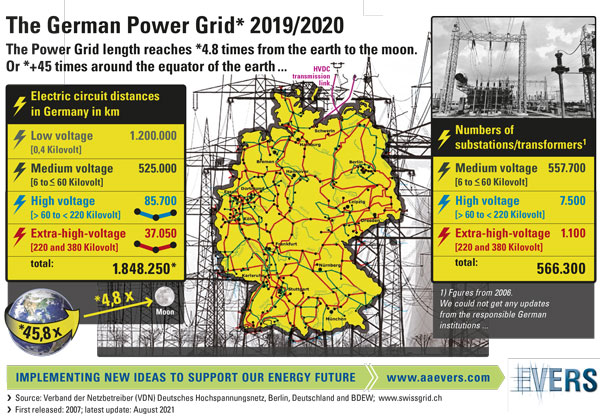
The German Power Grid* 2019/2020
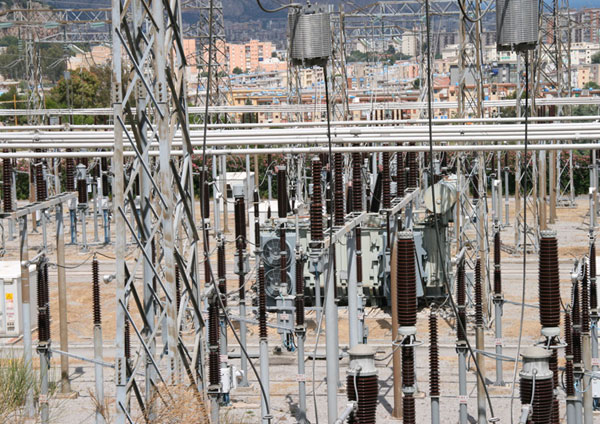
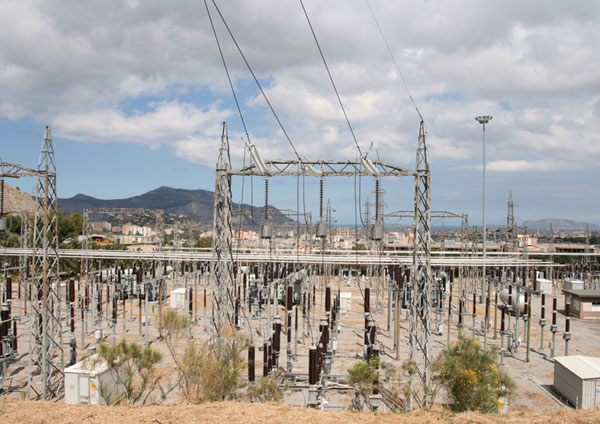
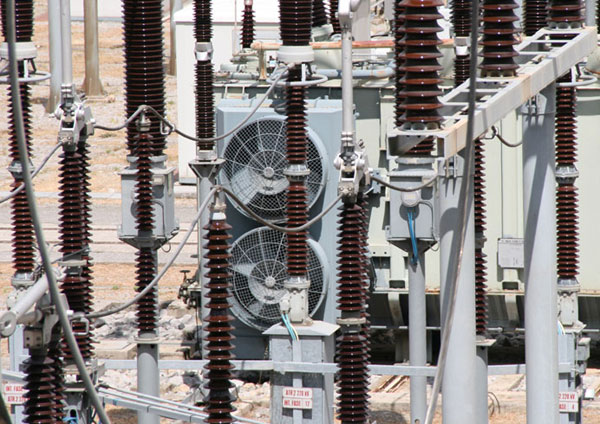
The German power grid has a total length of more than 1.8 million kilometers. This corresponds to 4.78 times the distance from the earth to the moon, or 45.8 times around the equator. It consists of four voltage levels. The lowest voltage level (low voltage of less than 1 kilovolt) is responsible for supplying households and smaller businesses. It has a total length of 1.190.000 kilometres. The various voltage levels are interconnected by 566,300 substations. Here, the voltage is converted 24/7 to a higher and lower voltage. In this process, the substations emit huge amounts of conversion heat. The German electricity grid in its present form is based on historical developments of the past centuries. It was and is not physically intended to feed fluctuating voltages and frequencies, as they come from so-called renewable energies. Electrical substation, Palermo, Italy
|